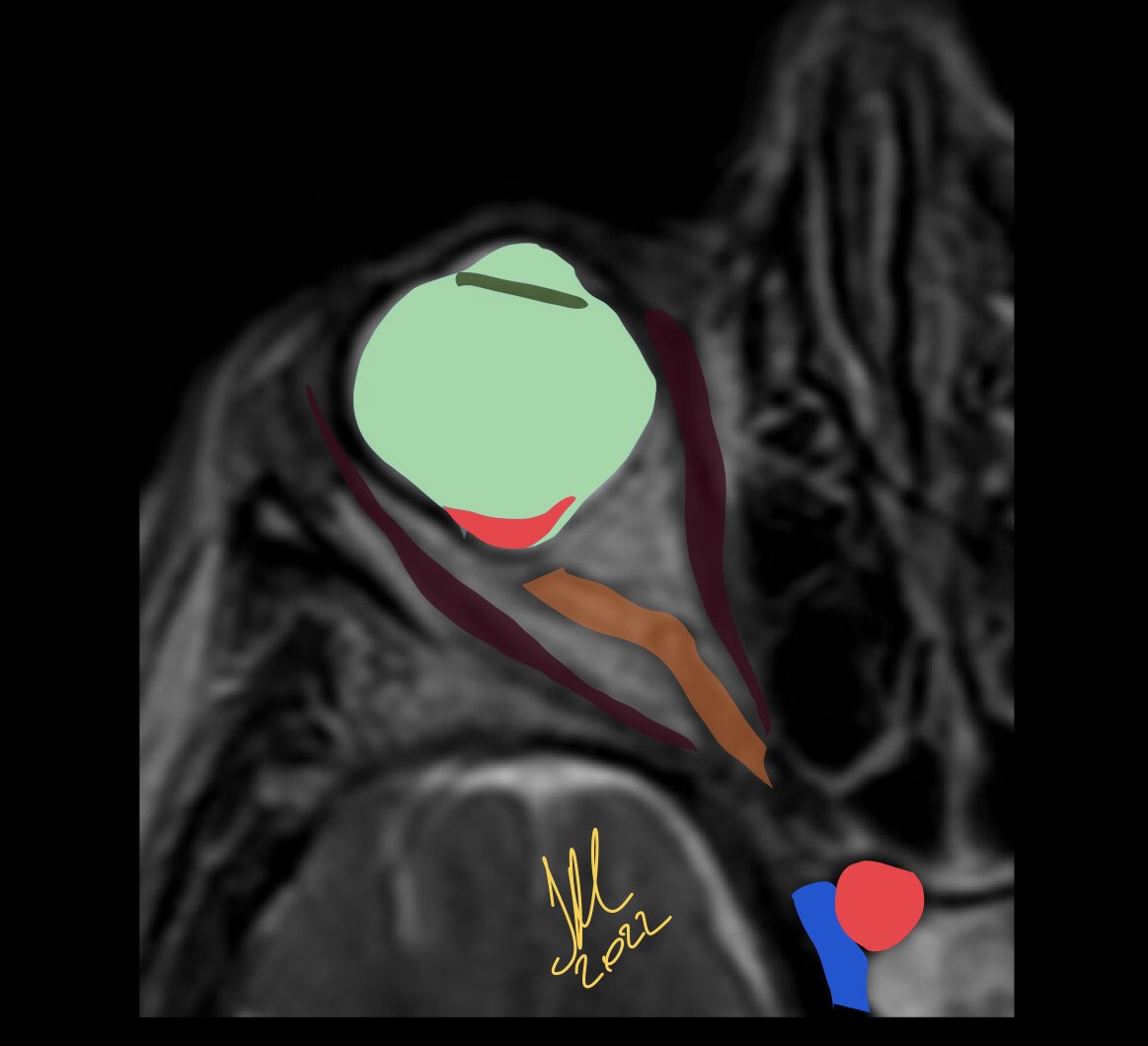
Posterior staphyloma is sine qua non of pathological myopia. It is characterized by disproportionate scleral ectasia with stretched conforming retinochoroidal layers. Conventionally, it has been classified into multiple types depending on location, although it usually involves the posterior pole of the eye. This outbulge, however, is a major risk factor for visually impairing maculopathy. PS can also be seen independent of high axial myopia.
As opposed to coloboma, staphyloma defect is located off-center from the optic disc, typically temporal to the disc.
Reference:
Eye Globe Abnormalities on MR and CT in Adults: An Anatomical Approach Korean J Radiol. 2016 Sep-Oct; 17(5): 664–673. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2016.17.5.664
Indian J Ophthalmol. 2017 Oct; 65(10): 1030–1032. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_415_17
Gaillard, F., Botz, B. Staphyloma. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org. (accessed on 25 Mar 2022) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-4009