
Parotid gland is an uncommon metastatic site for non-head and neck primary tumours. Metastatic tumours found in the parotid gland more commonly originate from primary head and neck
cancers, while those originating from non-head and neck sites constitute 13% of metastatic lesions found in the parotid. Of the various non-head and neck primary tumours, lung cancer is the most common site of origin with other previously reported sites include renal, breast, colon and gynaecological carcinomas, as well as lymphomas.
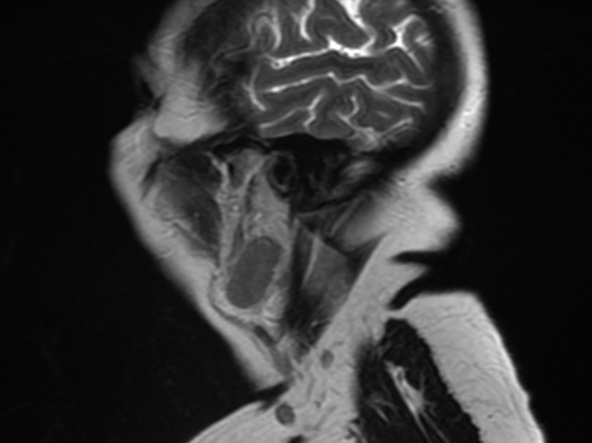
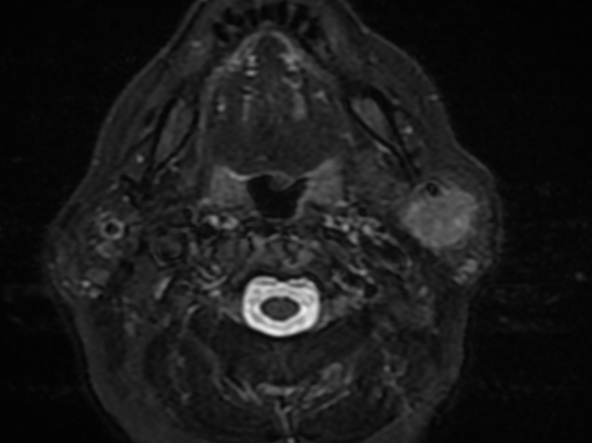
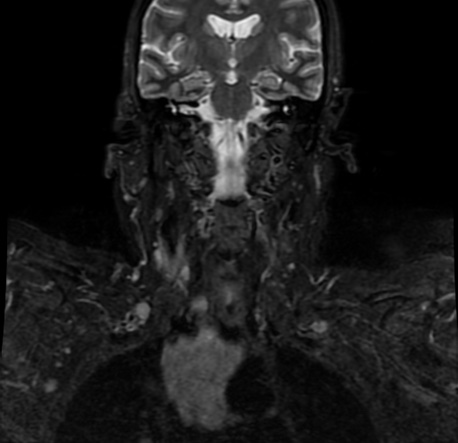
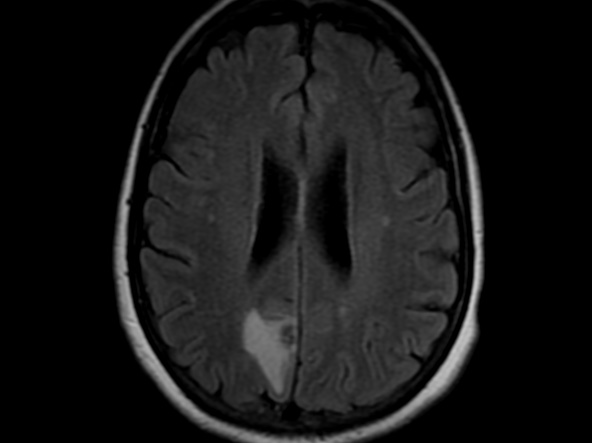
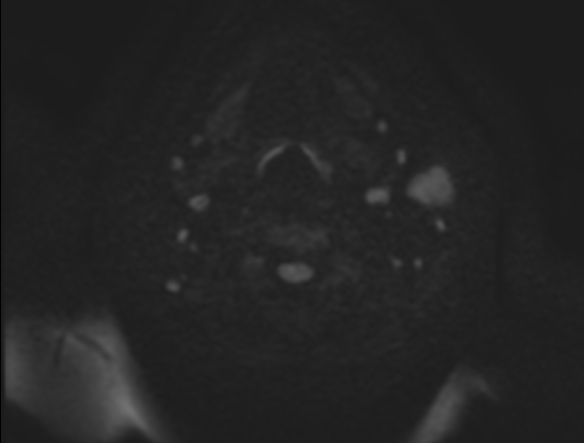
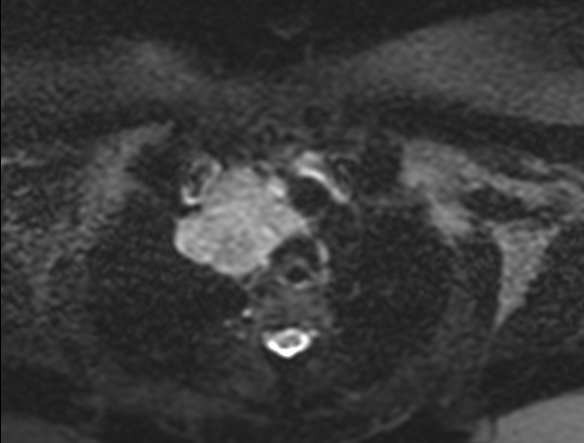
It is postulated that these infraclavicular tumours usually affect the parotid parenchyma by means
of haematogenous spread, while primary head and neck malignancies tend to spread to the parotid lymph nodes via the lymphatics.
MTS involving males with a median age of 60 years (range 40–74 years).
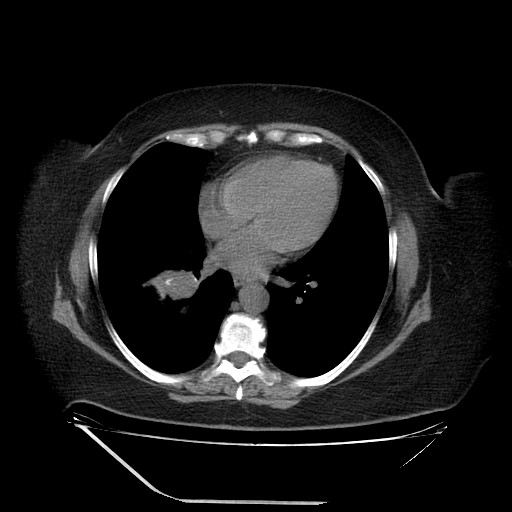
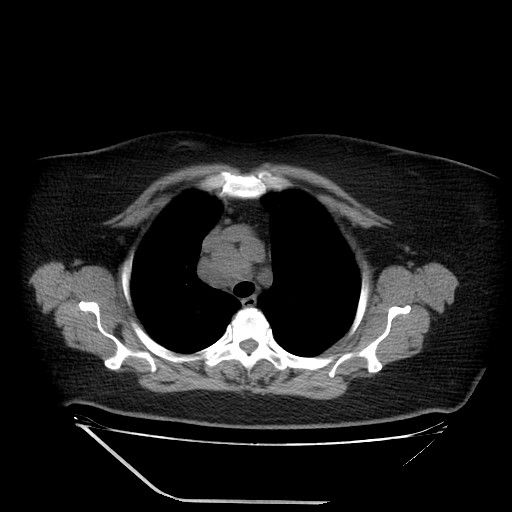
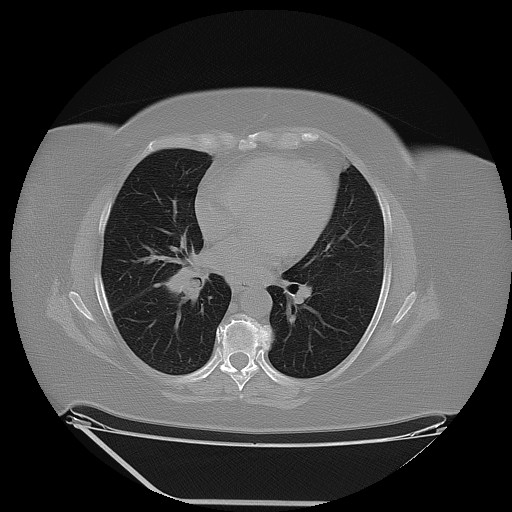
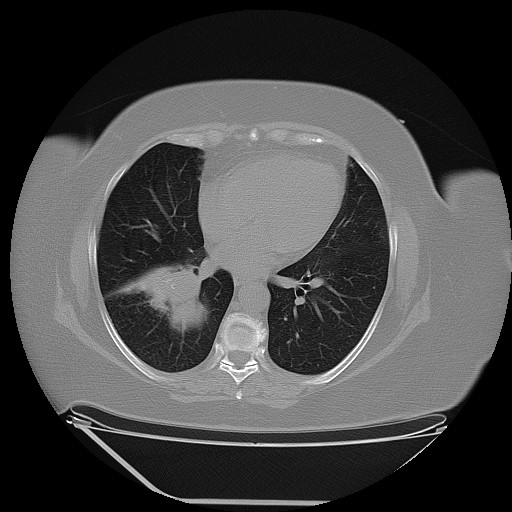
Although it is extremely rare, a potential metastasis of lung cancer should not be ignored in the diagnosis of a parotid tumor. Preoperative routine examinations such as a chest X-ray and lung CT, may play an important role in the differential diagnosis.
Reference:
doi:10.1136/bcr-2021-246779