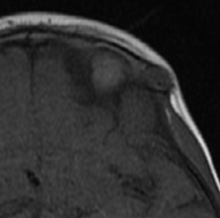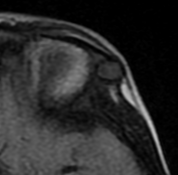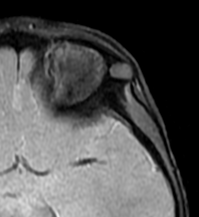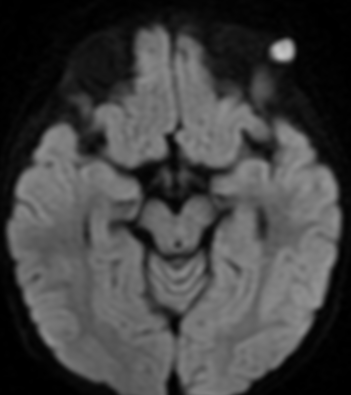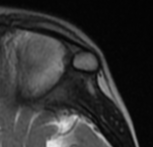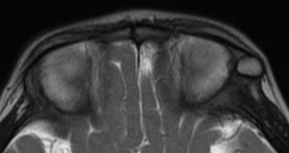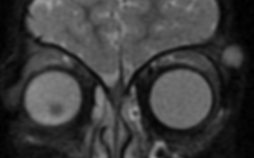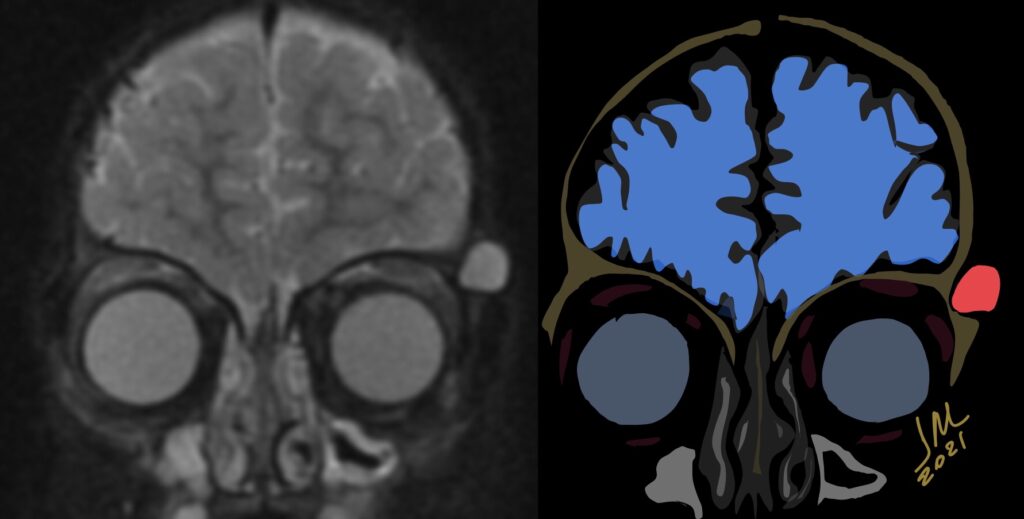
10% of intracranial epidermoids are extradural, being encountered most often in the skull as intradiploic masses in the temporal, occipital, parietal and frontal bones. Most manifest as painless, visible masses and are usually found along the lines of embryologic fusion; the zygomaticofrontal and the frontoethmoidal sutures
On MRI, epidermoids are hypointense on T1 hyperintense on T2 and maybe the most important thing have high signal intensity on DWI.
Differential diagnoses include dermoid cysts, eosinophilic granulomas, cholesterol granulomas, hemangiomas, aneurysmal bone cysts, fibrous dysplasia and eosinophilic granuloma.